Let’s say you have a flexbox container with a button inside:
<div class="container">
<button class="button">Button</button>
</div>If you try to center align the button (child element) horizontally with the justify-content property like this:
.container {
height: 300px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}Then the button’s (child element) height will stretch to whatever the height of the parent element is (in this case 300px):
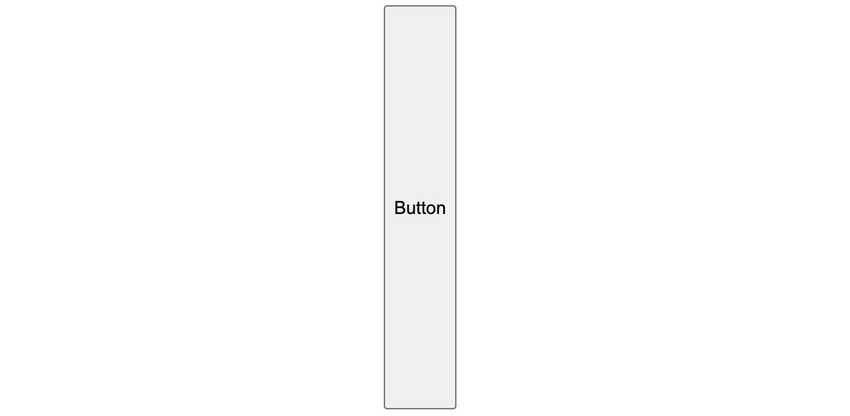
Which is probably not what you want!
There are a couple of ways to prevent the flex items (children of a flex container) from stretching vertically.
If you center align the flex items vertically with the align-items property, the stretch automatically goes away:
.container {
height: 300px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
/*Vertical center alignment:*/
align-items: center;
}
But what if you don’t want to vertically align your flex containers flex items?
Then you can use the CSS height property’s max-content value on the flex item:
.button {
height: max-content;
}
Now your flex items height will be determined by the height of its content, which in this button example is the text, which is 14px (+ the button’s default padding):
You can also use the align-self property on the flex item:
.button {
align-self: flex-start;
}This will yield the same result as using max-content in simple use cases, but it depends on your specific context (try both).